
USRCPU: The CPU usage by the process while running in user mode.SYSCPU: The CPU usage by the process while system handling.The lower section lists currently running processes and contains the following categories: The heading section of the command output provides an overview of system resources, including process and performance-related statistics and memory, disk, and network usage. z: Change the output color to highlight running processes.r: Change the nice value (priority) of a process by providing the PID.k: Kill a process by providing the PID.d: Change the output refresh rate to a user-defined value (in seconds).While the top command is running, use the following options to interact with it or change the output format: COMMAND: The name of the command that started the process.S: The status of the process - R (running) or S (sleeping).SHR: The total shared memory used by the process.RES: The resident (physical) memory amount used by the process.VIRT: The virtual memory amount used by the process.NI: The nice value of the process, with negative numbers indicating higher priority.PR: The scheduling priority for the process.USER: The name of the user running the process.The top command output contains the following categories: The output of the top command updates in real time, with the three-second default refresh rate. -u: Define a user whose processes you want to list.


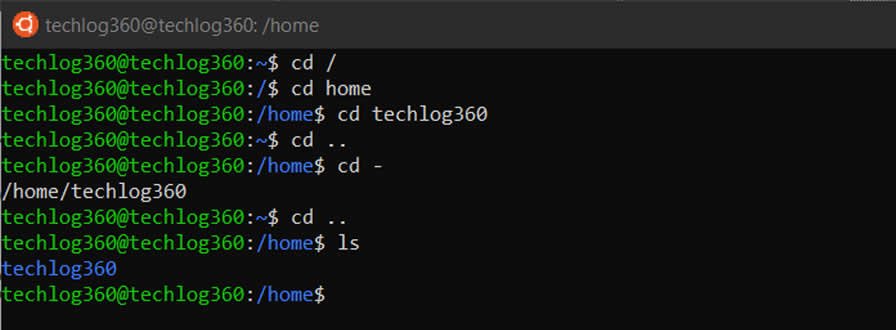
You can also combine the ps command with the pgrep command to identify individual processes. To list currently running processes, use the ps, top, htop, and atop Linux commands. Note: Learn more about terminating Linux processes in our guide to killing processes in Linux.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
